Satanic Knowledge Metal Tin Signs Print Poster 11 Sataniq Rules Of Earth Popular Science School Garden Hospital Farm Information Table Bar Garage Club Kitchen Home Wall Decoration Gift
FREE Shipping
Satanic Knowledge Metal Tin Signs Print Poster 11 Sataniq Rules Of Earth Popular Science School Garden Hospital Farm Information Table Bar Garage Club Kitchen Home Wall Decoration Gift
- Brand: Unbranded

Description
Satanism Today: An Encyclopedia of Religion, Folklore, and Popular Culture. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-292-9. Satanic Temple Founder Talks Atheistic Religion. The David Pakman Show. October 9, 2014 . Retrieved November 29, 2018. The Church of Satan weathered the Satanic Panic of the 1980s and ‘90s, with Lavey keeping a calm and low profile despite media attention. But the group faced challenges after Lavey’s death in 1997. Leadership went to Lavey’s partner Blanche Barton after a legal battle with his children. In 2001 Barton appointed author and Church member Peter H. Gilmore as high priest and his wife, church administrator Peggy Nadramia, as high priestess. Gilmore’s controversial claims that Church of Satan members were the only true Satanists led to a new wave of exoduses that saw departing church members creating their own offshoots. Luciferanism
Hallman, J.C. (2006). The Devil is a Gentleman: Exploring America's Religious Fringe. Random House. ISBN 978-1-4000-6172-3. Lewis, James R.; Tollefsen, Inga B. (2016). The Oxford Handbook of New Religious Movements, Volume 2. Oxford University Press. pp.441–453.a b c d e Oppenheimer, Mark (July 10, 2015). "A Mischievous Thorn in the Side of Conservative Christianity". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved November 29, 2018. Satan cast out by the archangel Michael, illustration by Gustave Doré from John Milton's Paradise Lost. (more) Later established as a nemesis of Jesus Christ in the New Testament, the final book of the Bible, Revelations, depicts him as the ultimate evil. It’s the Christian figure of Satan that Satanism directly references. Satan as Anti-Hero Dyrendal, Asbjørn; Lewis, James R.; Petersen, Jesper Aagaard (2016). The Invention of Satanism. Oxford University Press. p.220. ISBN 9780195181104.
Zaimov, Stoyan (July 30, 2015). "Satanic Temple Group Raising Money for On-Demand Abortions Echos Satanist History of 'Child Sacrifice,' Says Theologian". Christian Post . Retrieved November 29, 2018.During the early modern period, accusations of Devil worship became closely intertwined with accusations of witchcraft. While medieval witches had been regarded primarily as practitioners of maleficium, or supernaturally induced harm, in the early modern imagination witches were often believed to attend a witches’ sabbath where they proclaimed their allegiance to the Devil and engaged in cannibalistic infanticide. Across Christendom, tens of thousands of people were accused of being witches in this period and often were tortured to extract a confession. Between 40,000 and 60,000 were executed, most of them women. The Florida capitol's holiday display will include a festive message from the Satanic Temple". Washington Post. December 4, 2014 . Retrieved April 28, 2019. Satan’s first appearance wasn’t in Christianity. He began as the Zoroastrian Devil figure of Angra Mainyu or Ahriman, which opposed the Zoroastrian creator god and tempted humans. Satan is later portrayed in Jewish Kabbalism, which presents him as a demon who lives in a demonic realm. Satan, in the three major Abrahamic religions ( Judaism, Christianity, and Islam), the prince of evil spirits and adversary of God. Satan is traditionally understood as an angel (or sometimes a jinnī in Islam) who rebelled against God and was cast out of heaven with other “fallen” angels before the creation of humankind. Ezekiel 28:14–18 and Isaiah 14:12–17 are the key Scripture passages that support this understanding, and, in the New Testament, in Luke 10:18 Jesus states that he saw Satan fall like lightning from heaven. In all three major Abrahamic religions, Satan is identified as the entity (a serpent in the Genesis account) that tempted Eve to eat the forbidden fruit in the Garden of Eden and was thus the catalyst for the fall of humankind. (For further discussion of Satan in Islam, see Iblīs. For further discussion of Satan in Jewish folklore, see Samael.) Greene, Heather (December 21, 2021). "Catholic bishop criticizes Satanic Temple holiday display at Illinois Statehouse". Religion News Service . Retrieved December 22, 2021.
The Satanic Bible is a collection of essays, observations, and rituals published by Anton LaVey in 1969. It is the central religious text of LaVeyan Satanism, and is considered the foundation of its philosophy and dogma. [1] It has been described as the most important document to influence contemporary
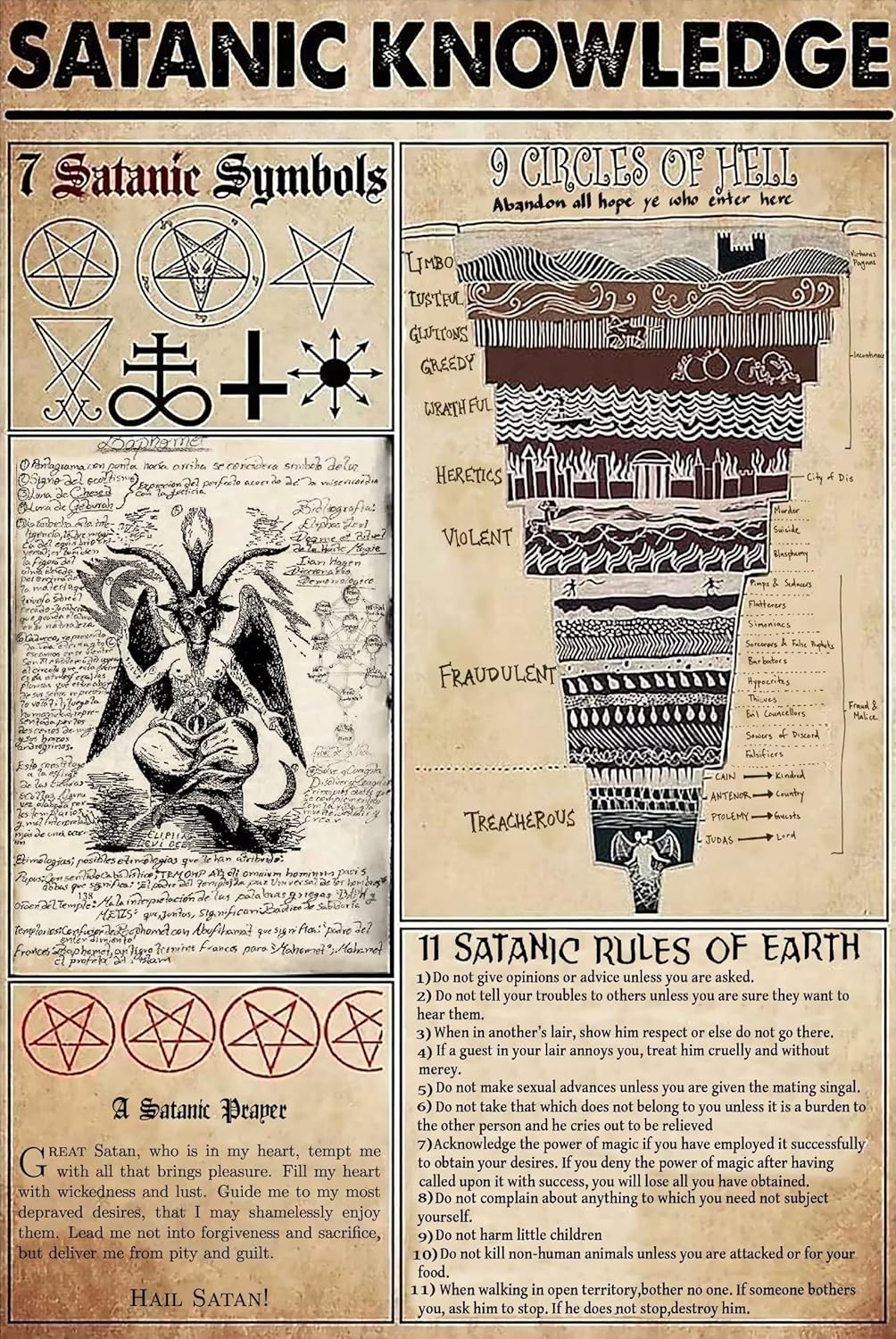
11 Satanic Rules & the 9 Satanic Sins
Social Darwinism and the concept of "human nature" are ideas that are prevalent throughout The Satanic Bible. LaVey describes Satanism as "a religion based on the universal traits of man," [78] and humans are described throughout as inherently carnal and animalistic. Each of the seven deadly sins is described as part of human's natural instinct, and are thus advocated. [79] Social Darwinism is particularly noticeable in The Book of Satan, where LaVey plagiarizes portions of Redbeard's Might Is Right, though it also appears throughout in references to man's inherent strength and instinct for self-preservation. [76] [80] LaVeyan Satanism has been described as "institutionalism of Machiavellian self-interest" because of many of these themes. [81] Influence [ edit ]
LaVey rejects the idea of prayer, instead urging Satanists to take action to fix a situation instead of asking for a solution. [52] The seven deadly sins are advocated, on the basis that they all lead to personal pleasure. He says that Satanism is a form of "controlled selfishness", in the sense that doing something to help another will, in turn, make one happy. The Golden Rule is again mentioned, and LaVey suggests altering it from "Do unto others as you would have them do unto you" to "Do unto others as they do unto you" so that if someone is treated poorly, he or she can respond viciously. [53] The Book of Lucifer also contains a list of "The Four Crown Princes of Hell" (Satan, Lucifer, Belial, and Leviathan) [54] and of seventy-seven " Infernal Names", representations of Satan from various cultures and religions. [55] They are the names that, according to LaVey, are most useful in Satanic rituals. [54] Most people imagine the devil as a red creature with horns and a pointed tail. But in your book you describe the many other visual iterations of Satan over the centuries. If you were to dress as Satan for Halloween, which depiction would you choose? Muzzatti, Stephen L. (2005). "Satanism". In Bosworth, Mary (ed.). Encyclopedia of Prisons and Correctional Facilities. Vol.2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Reference. pp.874–876. ISBN 978-1-4129-2535-8. Kaufman, Amanda. "Salem-based Satanic Temple challenges Texas abortion law, arguing religious freedom - The Boston Globe". BostonGlobe.com . Retrieved May 3, 2022. Artists in the Decadent movement like Félicien Rops placed Satanic imagery in paintings, influenced by writers like Baudelaire and Poe. Satan was also employed in writings from socialist leaders like Mikhail Bakunin and Karl Marx.
Show your support for independent, non-profit journalism with a gift this Giving Tuesday.
Brown, Louise (1 October 1989). "Alarming number of teenagers drawn to Satanism, experts say". Toronto Star. LaVey established his movement in the U.S. state of California through the founding of his Church of Satan on Walpurgisnacht of 1966, which he proclaimed to be "the Year One", Anno Satanas—the first year of the "Age of Satan". His ideas were heavily influenced by the ideas and writings of Friedrich Nietzsche, Ayn Rand and Arthur Desmond. The church grew under LaVey's leadership, with regional grottos being founded across the United States. A number of these seceded from the church to form independent Satanic organizations during the early 1970s. In 1975, LaVey abolished the grotto system, after which LaVeyan Satanism became a far less organized movement, although it remained greatly influenced by LaVey's writings. In the coming years, members of the church left it to establish their own organizations, also following LaVey's ideas, among them John Dewey Allee's First Church of Satan and Karla LaVey's First Satanic Church. THERE ARE SEVEN FUNDAMENTAL TENETS - TST". thesatanictemple.com. The Satanic Temple . Retrieved October 23, 2022. Though at some points LaVey refers to Satan as a physical being, this is intended to encourage the Satanist's "rational self-interest." [74] Science [ edit ] In contrast to these atheistic groups, there have also been modern Satanists who regard Satan or Lucifer as having a literal existence. One of the first organized groups to take this stance, the Temple of Set, was formed by Michael Aquino and other former members of LaVey’s Church in 1975. Unlike the Church of Satan, Aquino’s Temple maintained that Satan’s real identity was Set, a god drawn from the pantheon of ancient Egypt, thus shifting the organization away from its Satanic origins and toward modern Paganism. By the end of the 20th century, increasing numbers of people were considering themselves to be theistic Satanists. These individuals were typically solitary practitioners, communicating with one another through the Internet, rather than members of a single church.
- Fruugo ID: 258392218-563234582
- EAN: 764486781913
-
Sold by: Fruugo
